2025
Mathias Vorbröcker; Oliver Antons; Julia C Arlinghaus
Industrial Data Space Research Konferenz
Service Oriented, Holonic and Multi-agent Manufacturing Systems for Industry of the Future. SOHOMA 2024. Studies in Computational Intelligence, Bd. 1197, Springer, 2025, ISBN: 978-3-031-85316-6.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Schlagwörter: Data analytics, Data Space, Gaia-X, IDS
@conference{vorbrocker2025industrial,
title = {Industrial Data Space Research},
author = {Mathias Vorbr\"{o}cker and Oliver Antons and Julia C Arlinghaus},
editor = {Springer, Cham},
url = {https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-031-85316-6_12},
doi = {10.1007/978-3-031-85316-6_12},
isbn = {978-3-031-85316-6},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-07-03},
urldate = {2025-07-03},
booktitle = {Service Oriented, Holonic and Multi-agent Manufacturing Systems for Industry of the Future. SOHOMA 2024. Studies in Computational Intelligence},
journal = {Service Oriented, Holonic and Multi-agent Manufacturing Systems for Industry of the Future: Proceedings of SOHOMA 2024},
volume = {1197},
pages = {163},
publisher = {Springer},
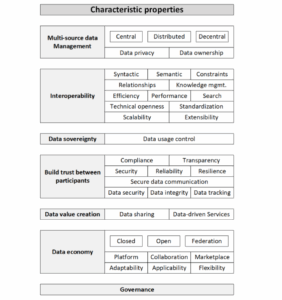
abstract = {In recent years, the topic of data spaces has been increasingly gaining traction. Multiple research initiatives, backed by industrial and government actors have introduced several data spaces for various industries and medicine, and beyond. In order to support value creation, public services and collaboration between a plethora of different participants of the data spaces, the sharing of information and building services and insights thereupon has been identified as key enabler. However, these initiatives differ in various properties from the initial idea for data spaces derived in research. In this article, we review the current state of literature regarding the concept of data spaces and the impact of European initiatives, namely International Data Spaces, Gaia-X and European Health Data Space, on the literature. Identifying characteristic properties of data spaces and its participants, we provide a general overview.},
keywords = {Data analytics, Data Space, Gaia-X, IDS},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {conference}
}
2021
Oliver Antons; Julia C. Arlinghaus
Adaptive self-learning distributed and centralized control approaches for smart factories Proceedings Article
In: S. 1577-1582, 2021, ISSN: 2212-8271, (54th CIRP CMS 2021 - Towards Digitalized Manufacturing 4.0).
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Schlagwörter: Autonomy, Autonomy & Decision-making Authority, Cyber-physical system, Data analytics, Decision-making, Discrete-event simulation, Distributed control, Industry 4.0, Multi-agent system, Self-learning, Smart factory
@inproceedings{ANTONS20211577,
title = {Adaptive self-learning distributed and centralized control approaches for smart factories},
author = {Oliver Antons and Julia C. Arlinghaus},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2212827121011641},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2021.11.266},
issn = {2212-8271},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-01-01},
urldate = {2021-01-01},
journal = {Procedia CIRP},
volume = {104},
pages = {1577-1582},
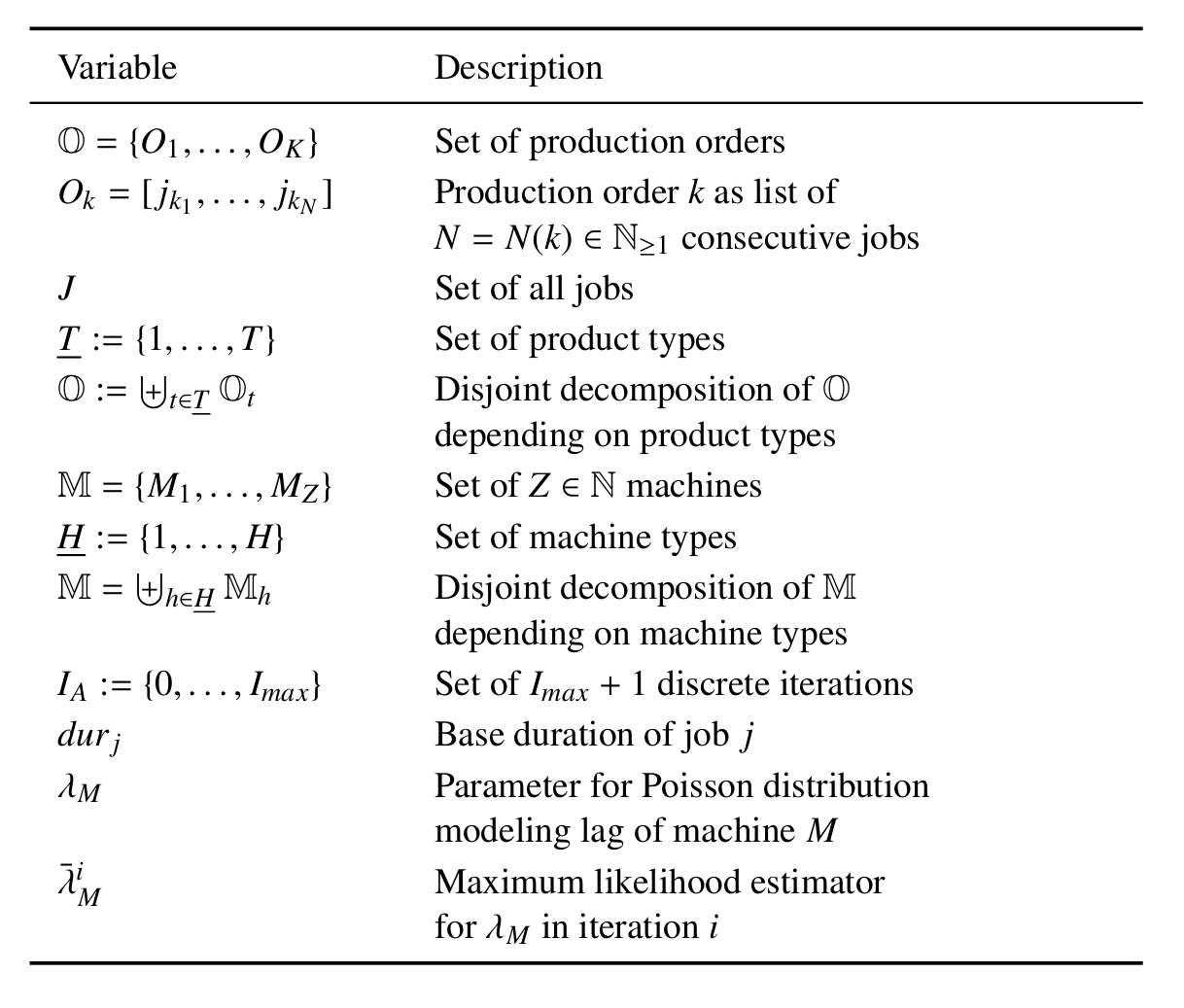
abstract = {The increasing application of cyber-physical systems creates a manufacturing environment in which the technical requirements for distributed control approaches, self-learning systems and analytics of previously untapped data are given. While distributed control approaches are capable to evaluate this information locally and react immediately, centralized approaches react inertly to analyzed machine performance data. In this paper, we study the performance and ability to address the ever increasing challenges in industry of both types of control approaches within an established multi-agent based discrete event simulation.},
note = {54th CIRP CMS 2021 - Towards Digitalized Manufacturing 4.0},
keywords = {Autonomy, Autonomy \& Decision-making Authority, Cyber-physical system, Data analytics, Decision-making, Discrete-event simulation, Distributed control, Industry 4.0, Multi-agent system, Self-learning, Smart factory},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}