2021
Oliver Antons; Julia C. Arlinghaus
Distributed control for Industry 4.0 -A comparative simulation study Proceedings Article
In: pp. 516-521, 2021, ISSN: 2405-8963, (17th IFAC Symposium on Information Control Problems in Manufacturing INCOM 2021).
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Autonomy & Decision-making Authority, Control, Discrete-event simulation, Distributed control, Make-to-order, Manufacturing planning, Multi-agent system
@inproceedings{ANTONS2021516,
title = {Distributed control for Industry 4.0 -A comparative simulation study},
author = {Oliver Antons and Julia C. Arlinghaus},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405896321007801},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2021.08.059},
issn = {2405-8963},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-01-01},
urldate = {2021-01-01},
journal = {IFAC-PapersOnLine},
volume = {54},
number = {1},
pages = {516-521},
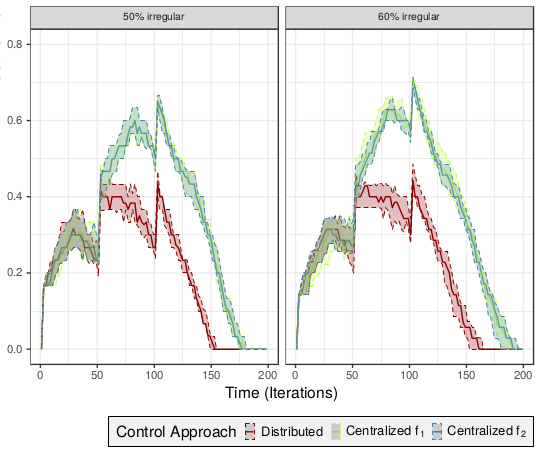
abstract = {The recent decades have seen various market changes that industrial manufactures need to address. Increasing individualization of products and rapid demand fluctuations require new control approaches. In this article, we study the performance of centralized and distributed control approaches with regard to work in progress in a make-to-order environment. We utilize a multi-agent system in a discrete-event simulation to model several control approaches and provide various insights into potential benefits of distributed control concepts given rapidly fluctuating manufacturing demand.},
note = {17th IFAC Symposium on Information Control Problems in Manufacturing INCOM 2021},
keywords = {Autonomy \& Decision-making Authority, Control, Discrete-event simulation, Distributed control, Make-to-order, Manufacturing planning, Multi-agent system},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
The recent decades have seen various market changes that industrial manufactures need to address. Increasing individualization of products and rapid demand fluctuations require new control approaches. In this article, we study the performance of centralized and distributed control approaches with regard to work in progress in a make-to-order environment. We utilize a multi-agent system in a discrete-event simulation to model several control approaches and provide various insights into potential benefits of distributed control concepts given rapidly fluctuating manufacturing demand.