2025
Tobias Bein; Oliver Antons; Julia C. Arlinghaus
Which PPC-Methods are implemented in Industry? - Yet another Review Journal Article
In: IFAC-PapersOnLine, vol. 59, no. 10, pp. 1005-1010, 2025, ISSN: 2405-8963, (11th IFAC Conference on Manufacturing Modelling, Management and Control MIM 2025).
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Control, Decision-making, decision-support systems, literature review, Production planning and control, research-practice gap, theory-practice gap
@article{BEIN20251005,
title = {Which PPC-Methods are implemented in Industry? - Yet another Review},
author = {Tobias Bein and Oliver Antons and Julia C. Arlinghaus},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405896325009310},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2025.09.170},
issn = {2405-8963},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-01-01},
urldate = {2025-01-01},
journal = {IFAC-PapersOnLine},
volume = {59},
number = {10},
pages = {1005-1010},
abstract = {This paper addresses the theory-practice gap in production planning and control (PPC), which describes the degree of applicability of academic research. We will measure this gap based on the reported application of academic research in industry. Therefore, this paper analyzes the current challenges that companies face in the area of PPC by reviewing empirical studies and relevant literature. We use our findings to draw conclusions about topics that are particularly helpful for the practical implementation of PPC methods and systems in industry. In addition, a literature analysis is carried out to provide a current overview on applied research. We show that applied research is still a term used in diverse settings and scenarios, ranging from purely theoretical works to practical implementations. Furthermore, the identified implementation studies are closely reviewed by comparing them to the analyzed topics currently of interest to practitioners. The results indicate that authors report on aspects of transparency as well as stakeholder-interaction, with the former being more prominently depicted.},
note = {11th IFAC Conference on Manufacturing Modelling, Management and Control MIM 2025},
keywords = {Control, Decision-making, decision-support systems, literature review, Production planning and control, research-practice gap, theory-practice gap},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2024
Andrea Somma; Oliver Antons; Alberto Petrillo; Stefania Santini; Teresa Murino
On the Verification of Distributed Control for Multi Job Shop Assignment Problem in Smart Manufacturing System Journal Article
In: IFAC-PapersOnLine, vol. 58, no. 19, pp. 217-222, 2024, ISSN: 2405-8963, (18th IFAC Symposium on Information Control Problems in Manufacturing INCOM 2024).
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Control, Digital-Model-Based Simulation, Distributed control, Multi-Job Shop Scheduling, Smart Manufacturing Planning
@article{SOMMA2024217,
title = {On the Verification of Distributed Control for Multi Job Shop Assignment Problem in Smart Manufacturing System},
author = {Andrea Somma and Oliver Antons and Alberto Petrillo and Stefania Santini and Teresa Murino},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405896324015866},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2024.09.171},
issn = {2405-8963},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-01-01},
urldate = {2024-01-01},
journal = {IFAC-PapersOnLine},
volume = {58},
number = {19},
pages = {217-222},
abstract = {The increasing need of product individualization and rapid demand fluctuation leads industrial manufacturers to leveraging new control solutions for production planning and control. Among these, distributed control approaches for the multi job shop scheduling problem could be a promising solution to make smart manufacturing systems more responsive to the market. In this context, this paper aims at investigating the effectiveness and the benefits of distributed control approaches for solving the multi job shop assignment problem on a real-world smart manufacturing process involving the production of high-vacuum solar panels. The validation is carried out by leveraging Cyber-Physical Systems modelling and a digital model-based procedure which, interacting with the physical plant, provides the proper job assignment in order to optimize the overall makespan and work-in-progress in a fully-distributed fashion.},
note = {18th IFAC Symposium on Information Control Problems in Manufacturing INCOM 2024},
keywords = {Control, Digital-Model-Based Simulation, Distributed control, Multi-Job Shop Scheduling, Smart Manufacturing Planning},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2022
Konstantin Büttner; Oliver Antons; Julia C. Arlinghaus
Applied Machine Learning for Production Planning and Control: Overview and Potentials Proceedings Article
In: 10th IFAC Conference on Manufacturing Modelling, Management and Control, pp. 6, Elsevier, 2022.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Control, Machine learning, Production control, Production Planning
@inproceedings{Buettner2022,
title = {Applied Machine Learning for Production Planning and Control: Overview and Potentials},
author = {Konstantin B\"{u}ttner and Oliver Antons and Julia C. Arlinghaus},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405896322021152},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2022.10.106},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-10-01},
urldate = {2022-10-01},
booktitle = {10th IFAC Conference on Manufacturing Modelling, Management and Control},
volume = {55},
number = {10},
pages = {6},
publisher = {Elsevier},
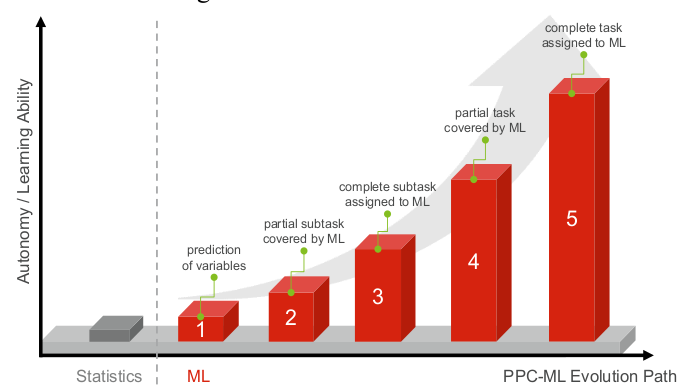
abstract = {Manufacturing companies are under constant pressure to increase efficiency and to achieve logistical objectives. Improving production planning and control (PPC) has significant impact on these efforts. At the same time, increasing complexity and dynamics of PPC environments make PPC more difficult. One way to cope with this situation is the application of machine learning (ML) methods. In this article, we therefore address the current state of PPC-ML research and show, based on the Aachen PPC model, in which PPC tasks and subtasks ML is already applied and to what degree the task is covered by ML. The analysis is limited to core and cross-sectional tasks of the Aachen PPC model, procurement and network tasks are not included. Furthermore, a broad analysis of the targeted data mining, business and logistic objectives is conducted. In addition, we also identify motivations which prompted researchers to apply ML in PPC. },
keywords = {Control, Machine learning, Production control, Production Planning},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Florian Knapp; Oliver Antons; Julia C. Arlinghaus
Opportunities for Synchronization in Manufacturing as Key Performance Indicator Proceedings Article
In: pp. 1467-1472, 2022, ISSN: 2212-8271, (Leading manufacturing systems transformation – Proceedings of the 55th CIRP Conference on Manufacturing Systems 2022).
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Control, Key Performance Indicators, Manufacturing, Manufacturing Networks, Production Planning, Synchronization
@inproceedings{KNAPP20221467,
title = {Opportunities for Synchronization in Manufacturing as Key Performance Indicator},
author = {Florian Knapp and Oliver Antons and Julia C. Arlinghaus},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2212827122004607},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2022.05.176},
issn = {2212-8271},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-01-01},
urldate = {2022-01-01},
journal = {Procedia CIRP},
volume = {107},
pages = {1467-1472},
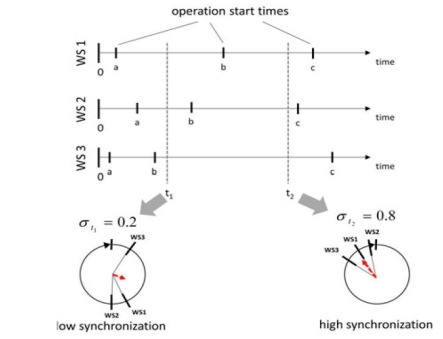
abstract = {In the complex and dynamic conditions of global markets it is increasingly challenging for manufacturing companies to find or identify new reliable and meaningful key performance indicators. Traditional performance indicators like lead time, inventory level, on-time delivery rate and capacity utilization are still in focus, but interdisciplinary research suggests the inclusion of more innovative performance indicators, such as synchronization. The synchronization level of a manufacturing system can be viewed twofold: logistic and physical synchronization. Physical synchronization is defined as "the rhythm and repetitive behaviour of production processes", while logistical synchronization describes "the coupling of work systems that are linked by material flows." Both types of synchronization correlate with the logistics performance of companies. Previous research on this topic has already provided first insights, highlighting potentials and fields of application. In this paper, we provide a structured literature review underlining relevant applications and explore their respective potentials. Thus, we show how synchronization effects can be exploited, and which systemic properties, such as network topology, characteristics and process time variation influence the occurrence of synchronization.},
note = {Leading manufacturing systems transformation \textendash Proceedings of the 55th CIRP Conference on Manufacturing Systems 2022},
keywords = {Control, Key Performance Indicators, Manufacturing, Manufacturing Networks, Production Planning, Synchronization},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
2021
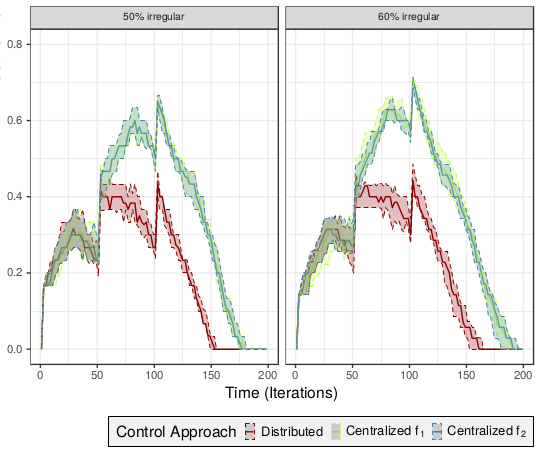
Oliver Antons; Julia C. Arlinghaus
Distributed control for Industry 4.0 -A comparative simulation study Proceedings Article
In: pp. 516-521, 2021, ISSN: 2405-8963, (17th IFAC Symposium on Information Control Problems in Manufacturing INCOM 2021).
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Autonomy & Decision-making Authority, Control, Discrete-event simulation, Distributed control, Make-to-order, Manufacturing planning, Multi-agent system
@inproceedings{ANTONS2021516,
title = {Distributed control for Industry 4.0 -A comparative simulation study},
author = {Oliver Antons and Julia C. Arlinghaus},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405896321007801},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2021.08.059},
issn = {2405-8963},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-01-01},
urldate = {2021-01-01},
journal = {IFAC-PapersOnLine},
volume = {54},
number = {1},
pages = {516-521},
abstract = {The recent decades have seen various market changes that industrial manufactures need to address. Increasing individualization of products and rapid demand fluctuations require new control approaches. In this article, we study the performance of centralized and distributed control approaches with regard to work in progress in a make-to-order environment. We utilize a multi-agent system in a discrete-event simulation to model several control approaches and provide various insights into potential benefits of distributed control concepts given rapidly fluctuating manufacturing demand.},
note = {17th IFAC Symposium on Information Control Problems in Manufacturing INCOM 2021},
keywords = {Autonomy \& Decision-making Authority, Control, Discrete-event simulation, Distributed control, Make-to-order, Manufacturing planning, Multi-agent system},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}