2024
Julia C. Arlinghaus; Oliver Antons
Planung und Steuerung für die digitale Produktion Book Chapter
In: Berlin Springer Vieweg, Heidelberg (Ed.): Handbuch Unternehmensorganisation, Springer Vieweg, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2024, ISBN: 978-3-642-45370-0.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Autonomous production control, Autonomy & Decision-making Authority, Cyber-physical system, Digitalization, Industry 4.0, Production planning and control, Smart manufacutring systems
@inbook{Arlinghaus2024,
title = {Planung und Steuerung f\"{u}r die digitale Produktion},
author = {Julia C. Arlinghaus and Oliver Antons},
editor = {Springer Vieweg, Berlin, Heidelberg},
url = {https://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1007/978-3-642-45370-0_63-2},
doi = {10.1007/978-3-642-45370-0_63-2},
isbn = {978-3-642-45370-0},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-07-01},
urldate = {2024-07-01},
booktitle = {Handbuch Unternehmensorganisation},
publisher = {Springer Vieweg, Berlin, Heidelberg},
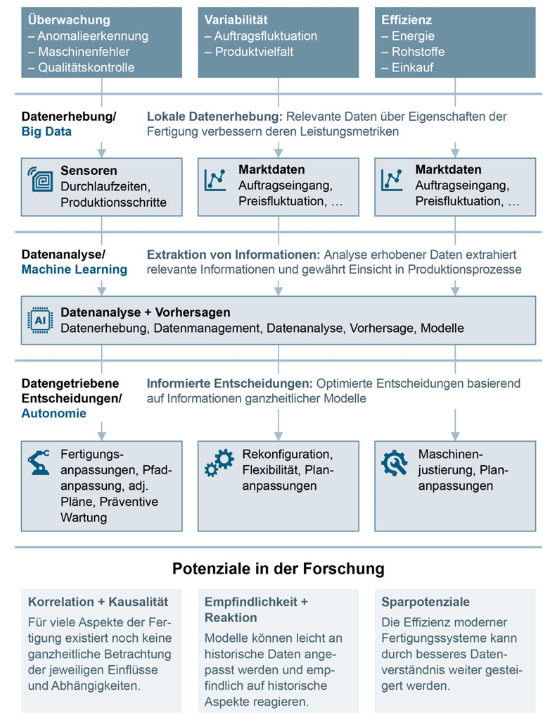
abstract = {Im vergangenen Jahrzehnt wurde die produzierende Industrie mit einem zunehmend volatileren Umfeld konfrontiert. Unterschiedlichste Krisen haben etablierte Lieferketten ersch\"{u}ttert und die Notwendigkeit resilienter und flexibler Produktionsplanung und -steuerung aufgezeigt. Zeitgleich hat eine voranschreitende Digitalisierung der Produktionsanlagen neue Herausforderungen, Potenziale und Chancen aufgeworfen. Cyber-physikalische Systeme und ein Industrial Internet of Things erm\"{o}glichen Digitale Zwillinge der Produktion und erf\"{u}llen die technischen Voraussetzungen f\"{u}r eine autonome Entscheidungsfindung auf einzelnen Produktionssystemen. In diesem Kontext stellt sich f\"{u}r Unternehmen eine fundamentale Frage der Organisation hinsichtlich der Architektur von Produktionsplanung und -steuerung. Mit zentralisierter sowie verteilter Produktionsplanung und -steuerung stehen Unternehmen zwei gegenl\"{a}ufige Ans\"{a}tze zur Verf\"{u}gung, die in diesem Beitrag n\"{a}her betrachtet werden.},
keywords = {Autonomous production control, Autonomy \& Decision-making Authority, Cyber-physical system, Digitalization, Industry 4.0, Production planning and control, Smart manufacutring systems},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inbook}
}
2022
Julia C. Arlinghaus; Oliver Antons
Management for Digitalization and Industry 4.0 Book Chapter
In: Berlin Springer, Heidelberg (Ed.): vol. Handbook Industry 4.0, pp. 927-948, 2022.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Digitalization, Industry 4.0
@inbook{Arlinghaus2022,
title = {Management for Digitalization and Industry 4.0},
author = {Julia C. Arlinghaus and Oliver Antons},
editor = {Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-64448-5_49},
doi = {10.1007/978-3-662-64448-5_49},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-06-23},
urldate = {2022-06-23},
volume = {Handbook Industry 4.0},
pages = {927-948},
abstract = {Global trends are changing how and what European companies manufacture. Progressive globalization and constant and immediate availability of relevant information through the Internet are not only changing the structure of global value networks but also compelling companies to operate under increasingly intense time, quality, innovation and cost pressure. Hence, the associated complexity of products, value networks and the planning and control processes is consequently growing. European companies are thus facing numerous seemingly conflicting challenges that their respective management has to reconcile.},
keywords = {Digitalization, Industry 4.0},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inbook}
}
2020
Julia C. Arlinghaus; Oliver Antons
Management für Digitalisierung und Industrie 4.0 Book Chapter
In: Handbuch Industrie 4.0: Recht, Technik, Gesellschaft, pp. 1121–1145, Springer, 2020.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Digitalization, Industry 4.0
@inbook{arlinghaus2020management,
title = {Management f\"{u}r Digitalisierung und Industrie 4.0},
author = {Julia C. Arlinghaus and Oliver Antons},
url = {https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-662-58474-3_58},
doi = {10.1007/978-3-662-58474-3_58},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-01-01},
urldate = {2020-01-01},
booktitle = {Handbuch Industrie 4.0: Recht, Technik, Gesellschaft},
pages = {1121--1145},
publisher = {Springer},
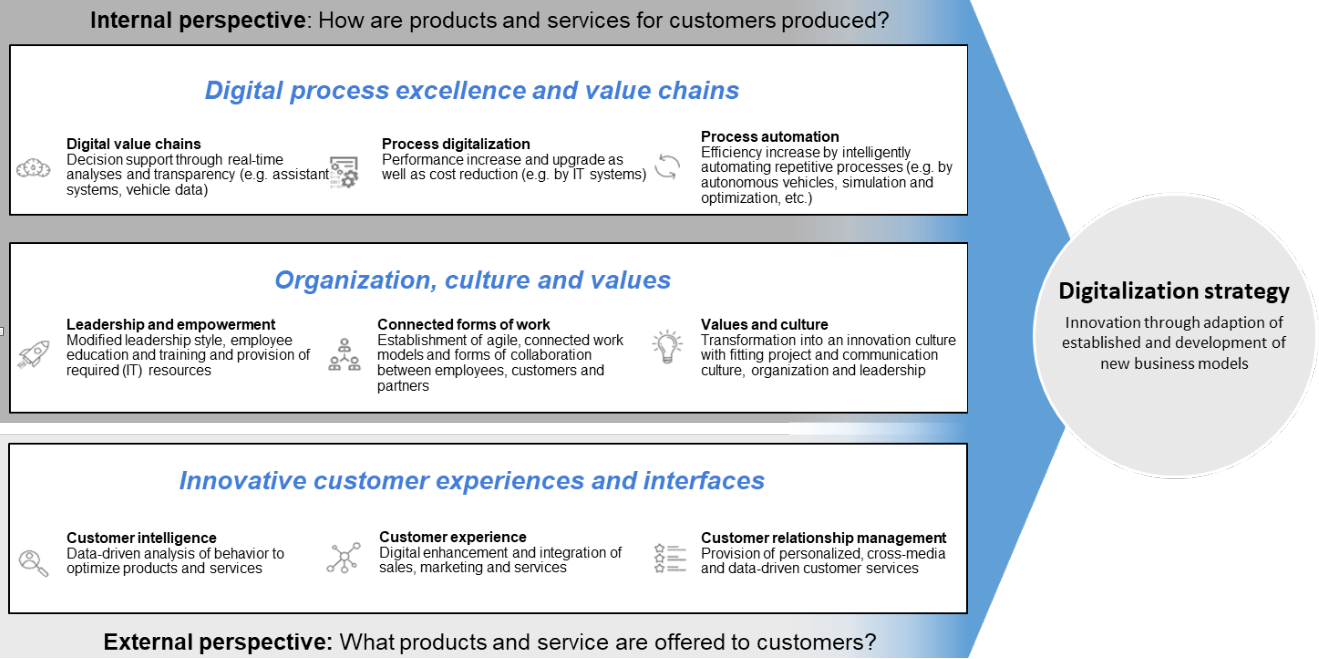
abstract = {Globale Trends ver\"{a}ndern wie und was europ\"{a}ische Unternehmen produzieren. Die fortschreitende Globalisierung und die permanente und direkte Verf\"{u}gbarkeit relevanter Informationen durch das Internet beeinflussen aber nicht nur die Struktur der globalen Wertsch\"{o}pfungsnetzwerke, sondern zwingen Unternehmen auch, unter immer gr\"{o}\sserem Zeit-, Qualit\"{a}ts-, Innovations- und Kostendruck zu arbeiten. Infolgedessen steigt die Komplexit\"{a}t der Produkte, der Wertsch\"{o}pfungsnetze und der dahinterliegenden Planungs- und Steuerungsprozesse. Vor diesem Hintergrund ist die unter dem Begriff "Industrie 4.0" zusammengefasste Vision zu einem Hoffnungstr\"{a}ger f\"{u}r die europ\"{a}ische Wirtschaft geworden. Dabei reicht diese Vision l\"{a}ngst \"{u}ber den Ursprung des Begriffs \textendash einer digitalisierten, intelligenten Fabrik \textendash hinaus und umfasst nahezu alle Gesch\"{a}ftsbereiche. Der damit f\"{u}r Unternehmen essenzielle Wandlungsprozess wird dabei meist als "Digitale Transformation" bezeichnet. Dabei handelt es sich jedoch nicht um eine einmalige Anpassung mit klarem Anfangs- und Endpunkt, sondern um einen fortw\"{a}hrenden Anpassungsprozess, den jedes Unternehmen f\"{u}r sich spezifisch gestalten und f\"{u}hren muss.},
keywords = {Digitalization, Industry 4.0},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inbook}
}
2019
Manuel Zimmermann; Eugenia Rosca; Oliver Antons; Julia C. Bendul
Supply chain risks in times of Industry 4.0: Insights from German cases Proceedings Article
In: pp. 1755–1760, Elsevier, 2019.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Digitalization, Industry 4.0, Risk factors, Risk management, Technologies
@inproceedings{zimmermann2019supply,
title = {Supply chain risks in times of Industry 4.0: Insights from German cases},
author = {Manuel Zimmermann and Eugenia Rosca and Oliver Antons and Julia C. Bendul},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405896319314363},
doi = {10.1016/j.ifacol.2019.11.455},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-01-01},
urldate = {2019-01-01},
journal = {IFAC-PapersOnLine},
volume = {52},
number = {13},
pages = {1755--1760},
publisher = {Elsevier},
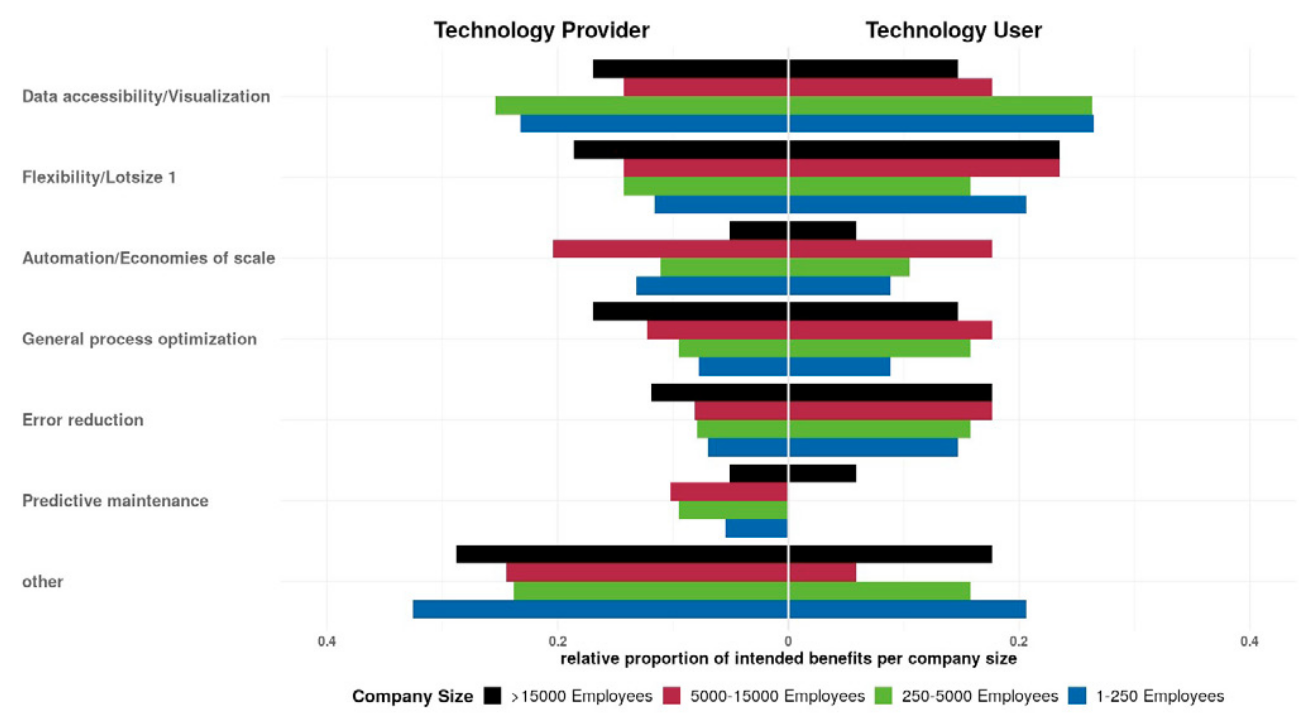
abstract = {This study investigates the impact of Industry 4.0 technologies on supply chain risks and examines which factors moderate this relationship. Drawing on a database of 300 Industry 4.0 projects all around Germany, the study explores empirically how Industry 4.0 technologies are employed to address various sources of various risks within production and supply chains. In this context, not only relevant technologies, existing risk factors and intended benefits are explored, but also factors that affect the relationship between these elements. Therefore, this paper shed light on the question which technologies are suitable and applicable for which user groups in which situations.},
keywords = {Digitalization, Industry 4.0, Risk factors, Risk management, Technologies},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Manuel Zimmermann; Oliver Antons; Julia C. Bendul
Determinants of risk factors and benefits associated with Industry 4.0 technologies: Insights from German cases Proceedings Article
In: EurOMA19, 2019.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Digitalization, Industry 4.0, Risk management
@inproceedings{Zimmermann-2019-ID693,
title = {Determinants of risk factors and benefits associated with Industry 4.0 technologies: Insights from German cases},
author = {Manuel Zimmermann and Oliver Antons and Julia C. Bendul},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-01-01},
urldate = {2019-01-01},
booktitle = {EurOMA19},
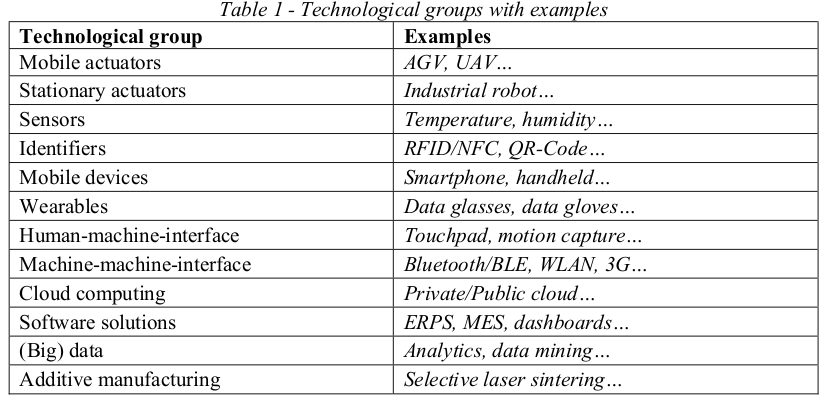
abstract = {This study investigates the application of current Industry 4.0 technologies as measures to counteract risk factors within companies and supply chains. Drawing on a database of more than 300 Industry 4.0 projects all around Germany, this study not only empirically explores which technologies and risk factors are currently relevant among practitioners \textendash but also evaluates the applicability of various technological solutions for the purpose of mitigating existing supply chain risks.},
keywords = {Digitalization, Industry 4.0, Risk management},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}