2024
Julia C. Arlinghaus; Oliver Antons
Planung und Steuerung für die digitale Produktion Book Chapter
In: Berlin Springer Vieweg, Heidelberg (Ed.): Handbuch Unternehmensorganisation, Springer Vieweg, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2024, ISBN: 978-3-642-45370-0.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Autonomous production control, Autonomy & Decision-making Authority, Cyber-physical system, Digitalization, Industry 4.0, Production planning and control, Smart manufacutring systems
@inbook{Arlinghaus2024,
title = {Planung und Steuerung f\"{u}r die digitale Produktion},
author = {Julia C. Arlinghaus and Oliver Antons},
editor = {Springer Vieweg, Berlin, Heidelberg},
url = {https://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1007/978-3-642-45370-0_63-2},
doi = {10.1007/978-3-642-45370-0_63-2},
isbn = {978-3-642-45370-0},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-07-01},
urldate = {2024-07-01},
booktitle = {Handbuch Unternehmensorganisation},
publisher = {Springer Vieweg, Berlin, Heidelberg},
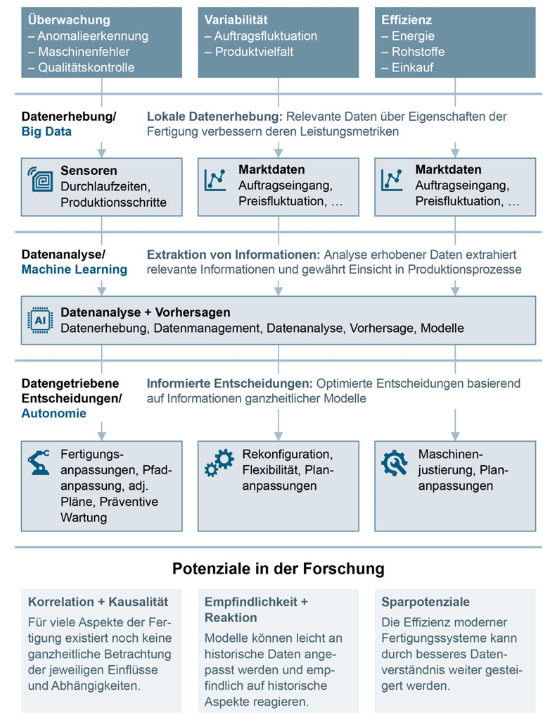
abstract = {Im vergangenen Jahrzehnt wurde die produzierende Industrie mit einem zunehmend volatileren Umfeld konfrontiert. Unterschiedlichste Krisen haben etablierte Lieferketten ersch\"{u}ttert und die Notwendigkeit resilienter und flexibler Produktionsplanung und -steuerung aufgezeigt. Zeitgleich hat eine voranschreitende Digitalisierung der Produktionsanlagen neue Herausforderungen, Potenziale und Chancen aufgeworfen. Cyber-physikalische Systeme und ein Industrial Internet of Things erm\"{o}glichen Digitale Zwillinge der Produktion und erf\"{u}llen die technischen Voraussetzungen f\"{u}r eine autonome Entscheidungsfindung auf einzelnen Produktionssystemen. In diesem Kontext stellt sich f\"{u}r Unternehmen eine fundamentale Frage der Organisation hinsichtlich der Architektur von Produktionsplanung und -steuerung. Mit zentralisierter sowie verteilter Produktionsplanung und -steuerung stehen Unternehmen zwei gegenl\"{a}ufige Ans\"{a}tze zur Verf\"{u}gung, die in diesem Beitrag n\"{a}her betrachtet werden.},
keywords = {Autonomous production control, Autonomy \& Decision-making Authority, Cyber-physical system, Digitalization, Industry 4.0, Production planning and control, Smart manufacutring systems},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inbook}
}
2023
Oliver Antons; Julia C. Arlinghaus
Maximum Likelihood and Neural Network Estimators for Distributed Production Control Proceedings Article
In: IFAC-PapersOnLine , pp. 10327-10332, 2023, ISSN: 2405-8963, (22nd IFAC World Congress).
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Autonomy & Decision-making Authority, Cyber-physical system, Distributed control, Machine learning, Production planning and control, Smart manufacutring systems
@inproceedings{nokey,
title = {Maximum Likelihood and Neural Network Estimators for Distributed Production Control},
author = {Oliver Antons and Julia C. Arlinghaus},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405896323014210},
doi = {10.1016/j.ifacol.2023.10.1038},
issn = {2405-8963},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-07-14},
urldate = {2023-07-14},
booktitle = {IFAC-PapersOnLine },
volume = {56},
number = {2},
pages = {10327-10332},
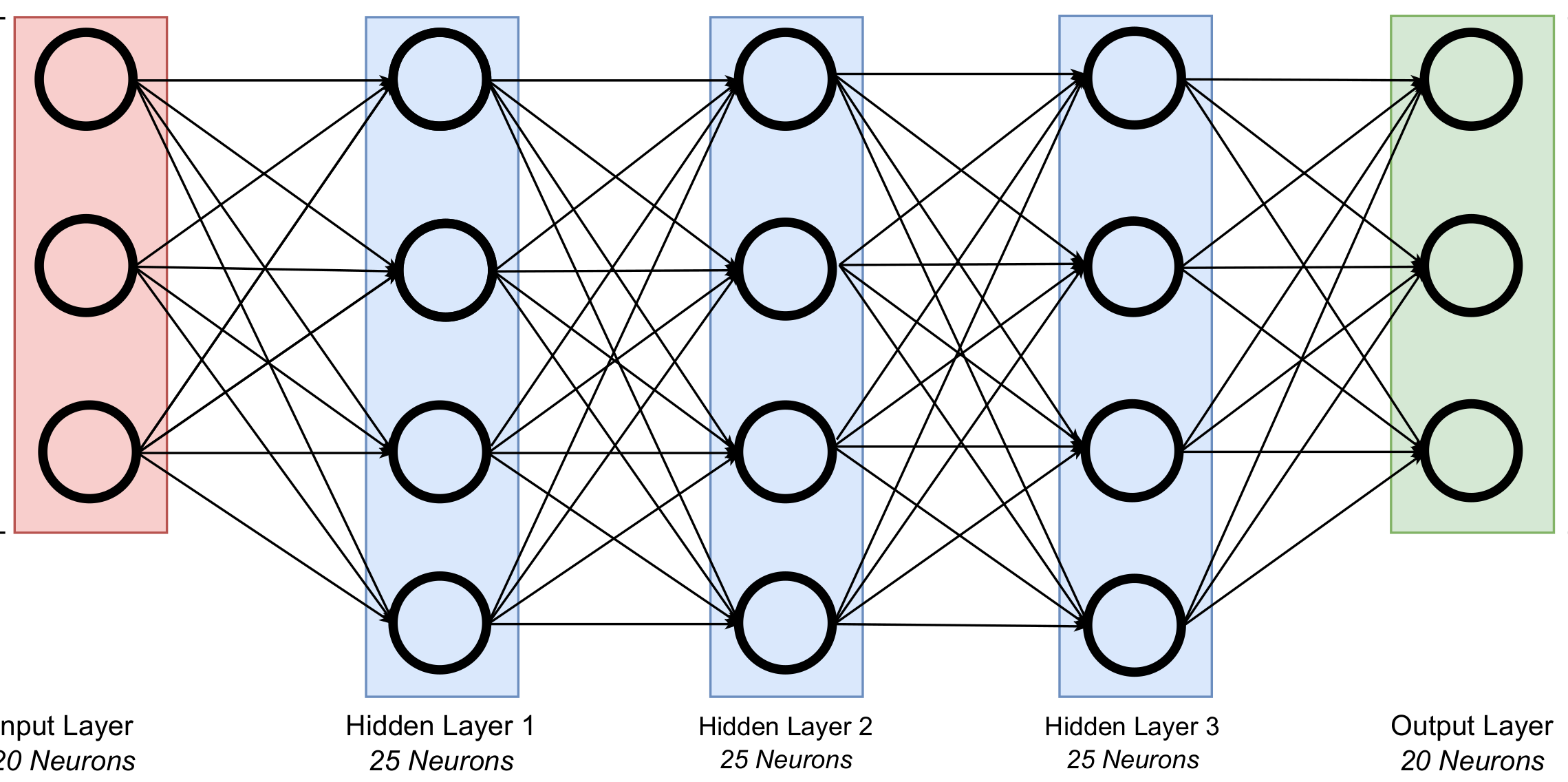
abstract = {Cyber-physical systems have become increasingly common in recent years, providing a multitude of information regarding production processes. At the same time, increasing volatilities, uncertainties, complexity and ambiguity (VUCA) are challenging existing production control approaches for manufacturing networks. Data-driven control approaches are an avenue to address VUCA, but require further study in research and practice. We utilize a multi-agent based discrete-event simulation to compare the aptitudes of a maximum likelihood and neural network based estimator for distributed production control, and provide insights into application of machine learning to address ever increasing information and VUCA.},
note = {22nd IFAC World Congress},
keywords = {Autonomy \& Decision-making Authority, Cyber-physical system, Distributed control, Machine learning, Production planning and control, Smart manufacutring systems},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
2021
Oliver Antons; Julia C. Arlinghaus
Adaptive self-learning distributed and centralized control approaches for smart factories Proceedings Article
In: pp. 1577-1582, 2021, ISSN: 2212-8271, (54th CIRP CMS 2021 - Towards Digitalized Manufacturing 4.0).
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Autonomy, Autonomy & Decision-making Authority, Cyber-physical system, Data analytics, Decision-making, Discrete-event simulation, Distributed control, Industry 4.0, Multi-agent system, Self-learning, Smart factory
@inproceedings{ANTONS20211577,
title = {Adaptive self-learning distributed and centralized control approaches for smart factories},
author = {Oliver Antons and Julia C. Arlinghaus},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2212827121011641},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2021.11.266},
issn = {2212-8271},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-01-01},
urldate = {2021-01-01},
journal = {Procedia CIRP},
volume = {104},
pages = {1577-1582},
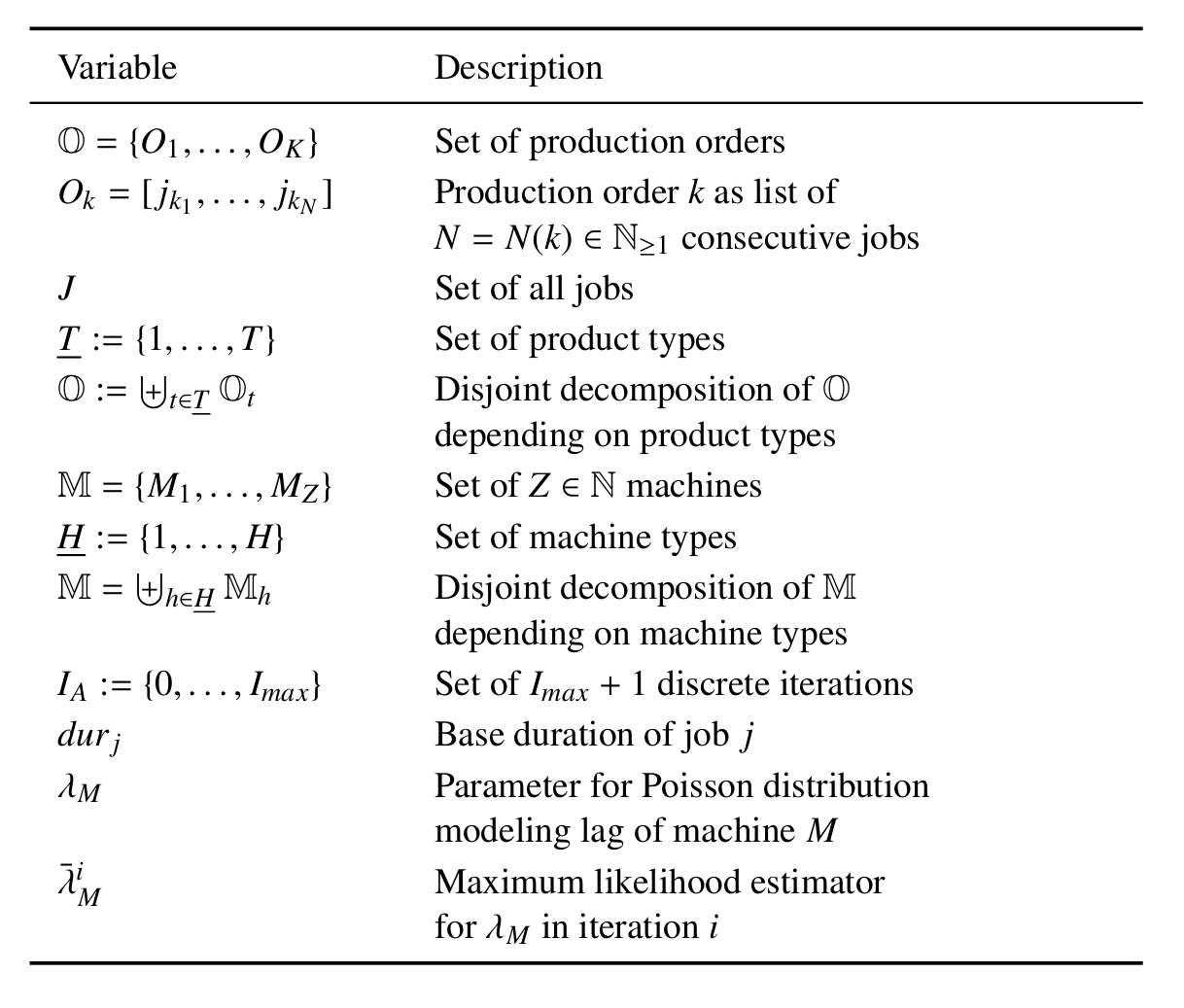
abstract = {The increasing application of cyber-physical systems creates a manufacturing environment in which the technical requirements for distributed control approaches, self-learning systems and analytics of previously untapped data are given. While distributed control approaches are capable to evaluate this information locally and react immediately, centralized approaches react inertly to analyzed machine performance data. In this paper, we study the performance and ability to address the ever increasing challenges in industry of both types of control approaches within an established multi-agent based discrete event simulation.},
note = {54th CIRP CMS 2021 - Towards Digitalized Manufacturing 4.0},
keywords = {Autonomy, Autonomy \& Decision-making Authority, Cyber-physical system, Data analytics, Decision-making, Discrete-event simulation, Distributed control, Industry 4.0, Multi-agent system, Self-learning, Smart factory},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
2020
Oliver Antons; Julia C. Arlinghaus
Designing decision-making authorities for smart factories Proceedings Article
In: pp. 316–322, Elsevier, 2020.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Autonomy, Autonomy & Decision-making Authority, Cyber-physical system, Decision-making, Discrete-event simulation, Distributed control, Industry 4.0, Intelligent Product, Multi-agent system, Smart factory
@inproceedings{antons2020designing,
title = {Designing decision-making authorities for smart factories},
author = {Oliver Antons and Julia C. Arlinghaus},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2212827120306120},
doi = {10.1016/j.procir.2020.04.047},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-01-01},
urldate = {2020-01-01},
journal = {Procedia CIRP},
volume = {93},
pages = {316--322},
publisher = {Elsevier},
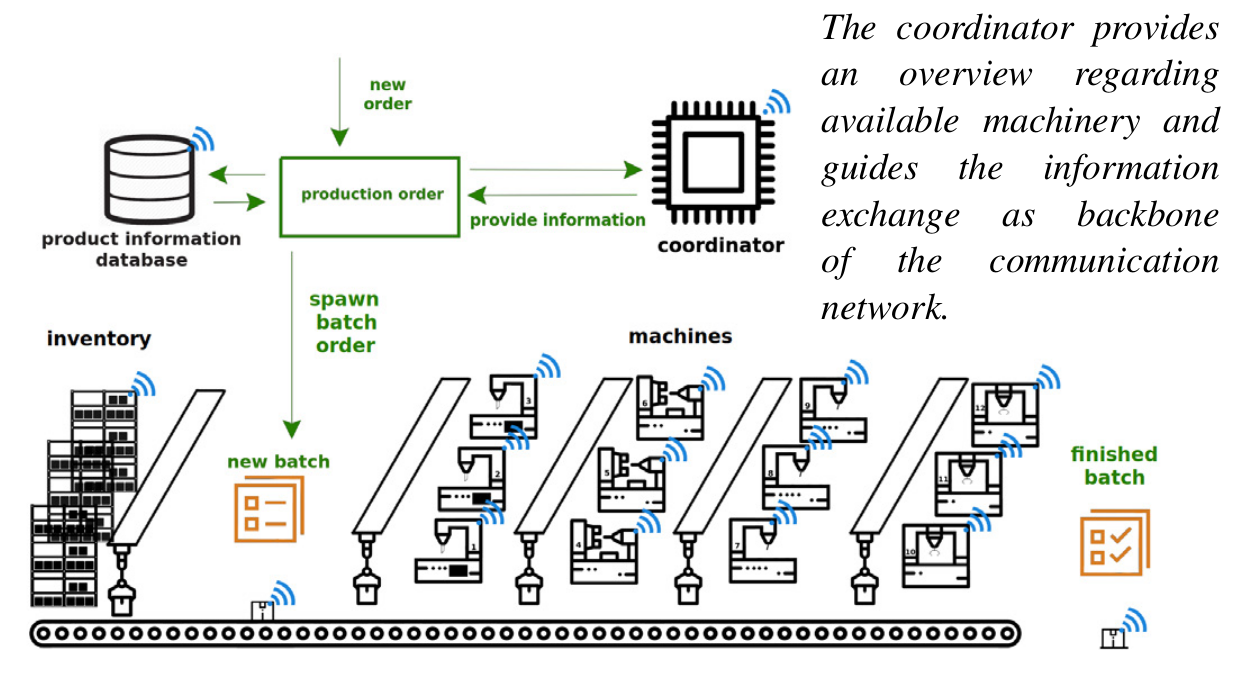
abstract = {Smart factories are an appealing vision, addressing ever increasing challenges in industry. Driven by advances in microcontroller, sensor and networking technologies, all entities, such as machines, products, load carriers, within a smart factory could become intelligent and able to assess their own situation and to attain their own goals successfully. However, local decision may exacerbate achieving global logistics performance due to the entities intrinsic selfishness. In this paper, we explore the trade-off between local decision-making and global performance management and derive first guidelines for the situation-specific design of a distributed control authority for smart factories.},
keywords = {Autonomy, Autonomy \& Decision-making Authority, Cyber-physical system, Decision-making, Discrete-event simulation, Distributed control, Industry 4.0, Intelligent Product, Multi-agent system, Smart factory},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}