2025

Tobias Bein; Ulf Bergmann; Oliver Antons; Julia C. Arlinghaus
Experience-Integrated Product Family Formation Using Clustering Algorithms Proceedings Article
In: Mizuyama, Hajime; Morinaga, Eiji; Nonaka, Tomomi; Kaihara, Toshiya; Cieminski, Gregor; Romero, David (Ed.): Advances in Production Management Systems. Cyber-Physical-Human Production Systems: Human-AI Collaboration and Beyond, pp. 311–325, Springer Nature Switzerland, Cham, 2025, ISBN: 978-3-032-03546-2.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Clustering, Human Decision-making, Production Planning, Production planning and control
@inproceedings{10.1007/978-3-032-03546-2_21,
title = {Experience-Integrated Product Family Formation Using Clustering Algorithms},
author = {Tobias Bein and Ulf Bergmann and Oliver Antons and Julia C. Arlinghaus},
editor = {Hajime Mizuyama and Eiji Morinaga and Tomomi Nonaka and Toshiya Kaihara and Gregor Cieminski and David Romero},
url = {https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-032-03546-2_21},
doi = {10.1007/978-3-032-03546-2_21},
isbn = {978-3-032-03546-2},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-08-30},
urldate = {2026-01-01},
booktitle = {Advances in Production Management Systems. Cyber-Physical-Human Production Systems: Human-AI Collaboration and Beyond},
pages = {311\textendash325},
publisher = {Springer Nature Switzerland},
address = {Cham},
abstract = {To ensure qualitatively sufficient results for the analysis of complex and diverse production programs, suitable analysis approaches must be utilized. As computer-based cluster algorithms become more widely used in this context, and as the demand for improved communication and coordination with the plant's stakeholders increases, there is an opportunity to integrate operator experience into clustering algorithms for production programs. This paper investigates whether and when the integration of operator experience is beneficial for this analysis. A single case study approach is utilized for this purpose, gaining insight and deriving general recommendations for integrating operator experience. While the operator's experience can enhance planning efficiency through tacit knowledge and insights in the form of inputs or feedback loops, it is susceptible to biases and must be checked by statistical analysis.},
keywords = {Clustering, Human Decision-making, Production Planning, Production planning and control},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}

Oliver Antons; Julia C. Arlinghaus
Manufacturing Network Topologies for Sustainable Production Proceedings Article
In: Mizuyama, Hajime; Morinaga, Eiji; Nonaka, Tomomi; Kaihara, Toshiya; Cieminski, Gregor; Romero, David (Ed.): Advances in Production Management Systems. Cyber-Physical-Human Production Systems: Human-AI Collaboration and Beyond, pp. 297–310, Springer Nature Switzerland, Cham, 2025, ISBN: 978-3-032-03546-2.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Manufacturing network topology, Production Planning, Production planning and control, Sustainability
@inproceedings{10.1007/978-3-032-03546-2_20,
title = {Manufacturing Network Topologies for Sustainable Production},
author = {Oliver Antons and Julia C. Arlinghaus},
editor = {Hajime Mizuyama and Eiji Morinaga and Tomomi Nonaka and Toshiya Kaihara and Gregor Cieminski and David Romero},
url = {https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-032-03546-2_20},
doi = {10.1007/978-3-032-03546-2_20},
isbn = {978-3-032-03546-2},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-08-30},
urldate = {2025-08-30},
booktitle = {Advances in Production Management Systems. Cyber-Physical-Human Production Systems: Human-AI Collaboration and Beyond},
pages = {297\textendash310},
publisher = {Springer Nature Switzerland},
address = {Cham},
abstract = {The linear transformation of finite resources to consumer electronics which are disregarded as waste after ever shorter lifespans is becoming notably problematic from both societal and ecological perspective. Increasing concerns for climate change and resource shortages as well as global supply chain disruptions highlight the deficits of linear economy. The alternative concept of circular economy introduces multiple sustainable strategies to traditional waste management at different points in a typical products lifespan, namely reduce, reuse, recycle, recovery, redesign, and remanufacturing (6R). However, circular economy has seen little adaption in practice. A major obstacle in the implementation of circular practices into production processes lies within the associated costs on the one hand, and the still relatively cheap access to virgin raw materials in large quantities from rather centralized supply systems on the other hand. Sustainable sourcing alternatives are typically characterized by limited local supply due to the corresponding catchment areas of recycling systems. Consequently, circular economy approaches lead to a more decentralized supply networks, increasing logistics costs and questioning established manufacturing topologies. In this article, we develop a minimal mixed-integer linear program in order to compare various spatial manufacturing topologies and supply networks with regard to linear and circular economy concepts. Considering the computational cost for established optimization concepts, we sketch a possible distributed approach to compare different manufacturing topologies and discuss their implications for practice and theory.},
keywords = {Manufacturing network topology, Production Planning, Production planning and control, Sustainability},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
2023
Tobias Benecke; Oliver Antons; Sanaz Mostaghim; Julia C. Arlinghaus
A Coevolution Approach for the Multi-objective Circular Supply Chain Problem Proceedings Article
In: 2023 IEEE Conference on Artificial Intelligence (CAI), pp. 222-223, 2023.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Complexity Theory, Costs, Production Planning, Profitability, Supply chain optimization
@inproceedings{10195126,
title = {A Coevolution Approach for the Multi-objective Circular Supply Chain Problem},
author = {Tobias Benecke and Oliver Antons and Sanaz Mostaghim and Julia C. Arlinghaus},
doi = {10.1109/CAI54212.2023.00103},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-01-01},
urldate = {2023-01-01},
booktitle = {2023 IEEE Conference on Artificial Intelligence (CAI)},
pages = {222-223},
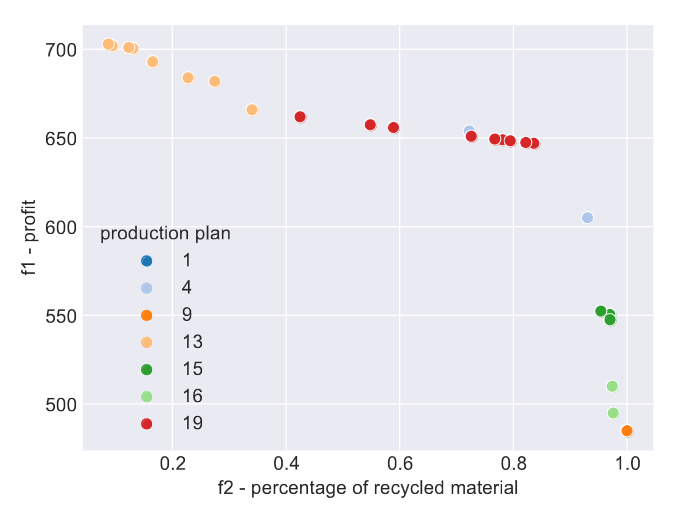
abstract = {As a more sustainable resource use is becoming of greater concern, moving towards a more circular economy seems promising. However, compared to the traditional, mostly linear production processes, this introduces new challenges, as reintroducing recycled materials into production also increases supply chain complexity and therefore cost. The circular supply chain (CSC) problem is modeling these challenges to find good tradeoff solutions between profitability and sustainable resource use. The optimization concerns the production planning and material sourcing of a production plant. This is a complex task due to their inherent dependencies. In this paper, we use a cooperative coevolutionary approach to optimize the CSC problem, by decomposing it to resolve the variable dependencies. Besides presenting the algorithm, a proof of concept evaluation is done to show its feasibility.},
keywords = {Complexity Theory, Costs, Production Planning, Profitability, Supply chain optimization},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
2022
Konstantin Büttner; Oliver Antons; Julia C. Arlinghaus
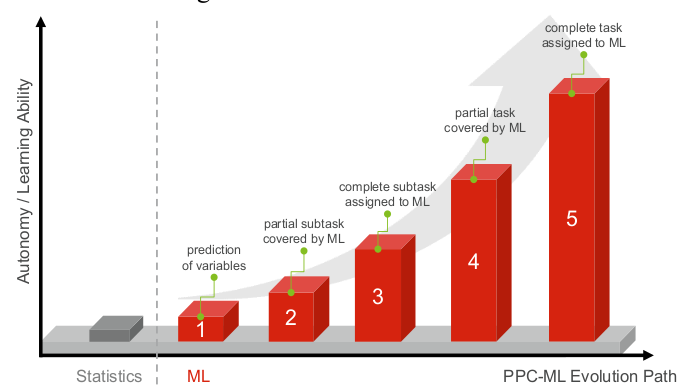
Applied Machine Learning for Production Planning and Control: Overview and Potentials Proceedings Article
In: 10th IFAC Conference on Manufacturing Modelling, Management and Control, pp. 6, Elsevier, 2022.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Control, Machine learning, Production control, Production Planning
@inproceedings{Buettner2022,
title = {Applied Machine Learning for Production Planning and Control: Overview and Potentials},
author = {Konstantin B\"{u}ttner and Oliver Antons and Julia C. Arlinghaus},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405896322021152},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2022.10.106},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-10-01},
urldate = {2022-10-01},
booktitle = {10th IFAC Conference on Manufacturing Modelling, Management and Control},
volume = {55},
number = {10},
pages = {6},
publisher = {Elsevier},
abstract = {Manufacturing companies are under constant pressure to increase efficiency and to achieve logistical objectives. Improving production planning and control (PPC) has significant impact on these efforts. At the same time, increasing complexity and dynamics of PPC environments make PPC more difficult. One way to cope with this situation is the application of machine learning (ML) methods. In this article, we therefore address the current state of PPC-ML research and show, based on the Aachen PPC model, in which PPC tasks and subtasks ML is already applied and to what degree the task is covered by ML. The analysis is limited to core and cross-sectional tasks of the Aachen PPC model, procurement and network tasks are not included. Furthermore, a broad analysis of the targeted data mining, business and logistic objectives is conducted. In addition, we also identify motivations which prompted researchers to apply ML in PPC. },
keywords = {Control, Machine learning, Production control, Production Planning},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Florian Knapp; Oliver Antons; Julia C. Arlinghaus
Opportunities for Synchronization in Manufacturing as Key Performance Indicator Proceedings Article
In: pp. 1467-1472, 2022, ISSN: 2212-8271, (Leading manufacturing systems transformation – Proceedings of the 55th CIRP Conference on Manufacturing Systems 2022).
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Control, Key Performance Indicators, Manufacturing, Manufacturing Networks, Production Planning, Synchronization
@inproceedings{KNAPP20221467,
title = {Opportunities for Synchronization in Manufacturing as Key Performance Indicator},
author = {Florian Knapp and Oliver Antons and Julia C. Arlinghaus},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2212827122004607},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2022.05.176},
issn = {2212-8271},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-01-01},
urldate = {2022-01-01},
journal = {Procedia CIRP},
volume = {107},
pages = {1467-1472},
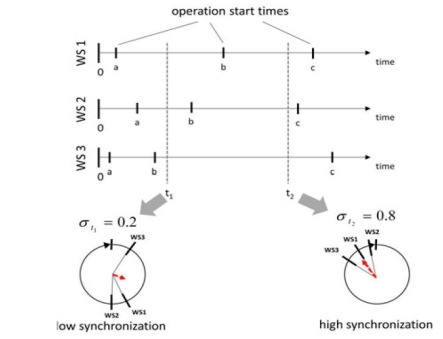
abstract = {In the complex and dynamic conditions of global markets it is increasingly challenging for manufacturing companies to find or identify new reliable and meaningful key performance indicators. Traditional performance indicators like lead time, inventory level, on-time delivery rate and capacity utilization are still in focus, but interdisciplinary research suggests the inclusion of more innovative performance indicators, such as synchronization. The synchronization level of a manufacturing system can be viewed twofold: logistic and physical synchronization. Physical synchronization is defined as "the rhythm and repetitive behaviour of production processes", while logistical synchronization describes "the coupling of work systems that are linked by material flows." Both types of synchronization correlate with the logistics performance of companies. Previous research on this topic has already provided first insights, highlighting potentials and fields of application. In this paper, we provide a structured literature review underlining relevant applications and explore their respective potentials. Thus, we show how synchronization effects can be exploited, and which systemic properties, such as network topology, characteristics and process time variation influence the occurrence of synchronization.},
note = {Leading manufacturing systems transformation \textendash Proceedings of the 55th CIRP Conference on Manufacturing Systems 2022},
keywords = {Control, Key Performance Indicators, Manufacturing, Manufacturing Networks, Production Planning, Synchronization},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}